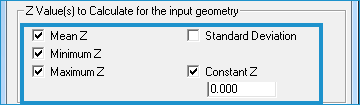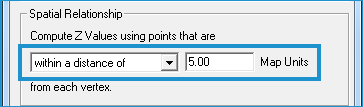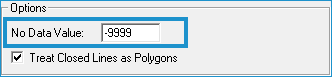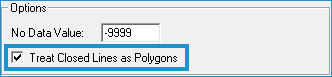

| Note Mean, Minimum, or Maximum values are defined by selecting a spatial relationship between the input geometry and the LAS points. Learn more about selecting a spatial relationship. |

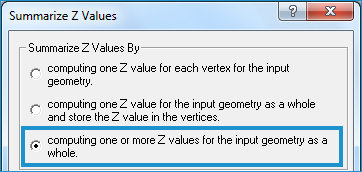
The Calculate Z by Vertex option is selected on the Summarize
Z Values dialog box. There are three situations in which
you will encounter this dialog:
(1) When setting up
an elevation conflaton task, you begin
by using the Elevation Conflation/Classify dialog
box, opened using the  button on the
LP360 Classify toolbar. Once you select the Layer
or Data
Set and then the features (in the Fields drop-down)
to use in the conflation, you will select a Conflation Method
for each listed feature in the Data Types table.
button on the
LP360 Classify toolbar. Once you select the Layer
or Data
Set and then the features (in the Fields drop-down)
to use in the conflation, you will select a Conflation Method
for each listed feature in the Data Types table.
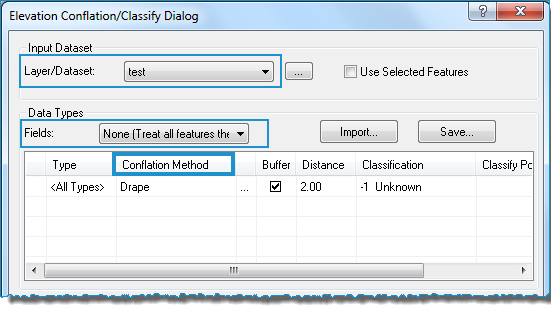
To select the conflation method, click on the cell under Conflation Method in the table next to one of the listed features. Another drop-down list will allow you to select a conflation method.

Select Summarize Z. The Summarize Z Values dialog will open.
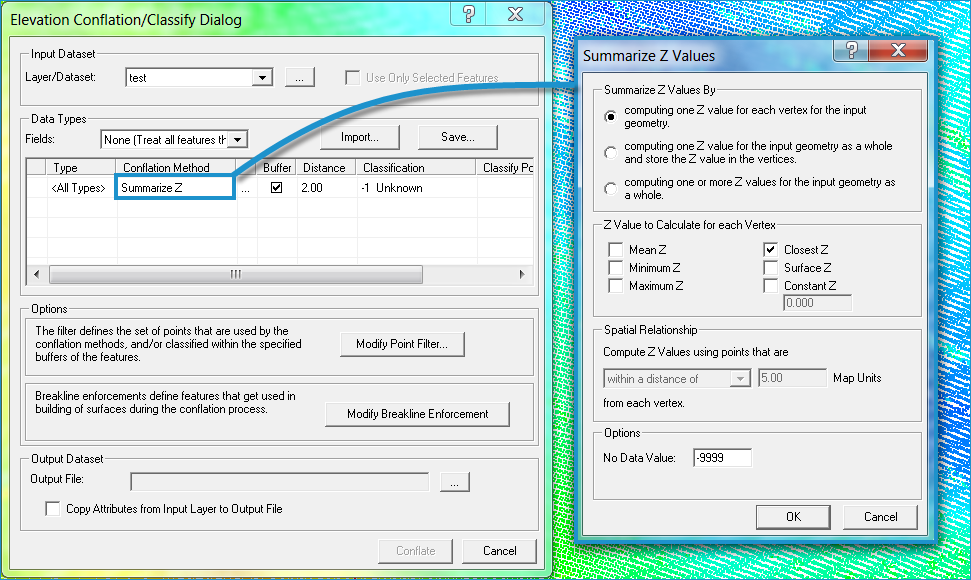
(2) When
digitizing features in LP360, you will likely have the LP360 Digitize
Breaklines toolbar open, and from this, you can manage conflation
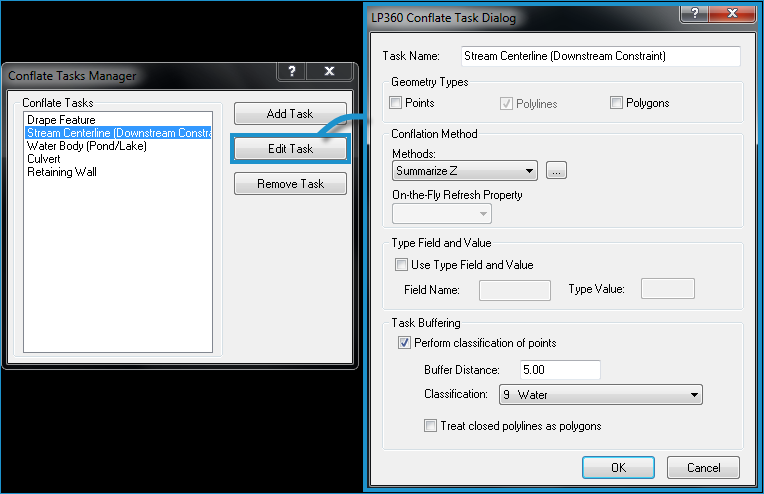
tasks using the Conflate Tasks Manager. (It opens
using the  button on the LP360 Digitize
Breaklines toolbar.)
button on the LP360 Digitize
Breaklines toolbar.)

When you select a task in the Conflate Tasks Manager dialog box and then click the Edit Task button, the LP360 Conflate Task Dialog opens, allowing you to further define a conflation task, including the Conflation Method.
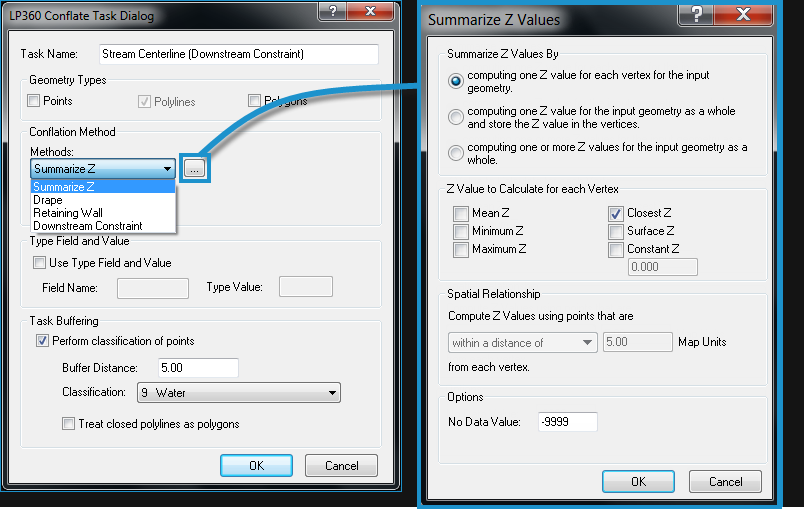
In the Conflation Method
drop-down, select Summarize Z and
then click the 
(3) When selecting "Summarize Z Values" from the Conflation Method drop-down list in the Conflation Point Cloud Task property page.