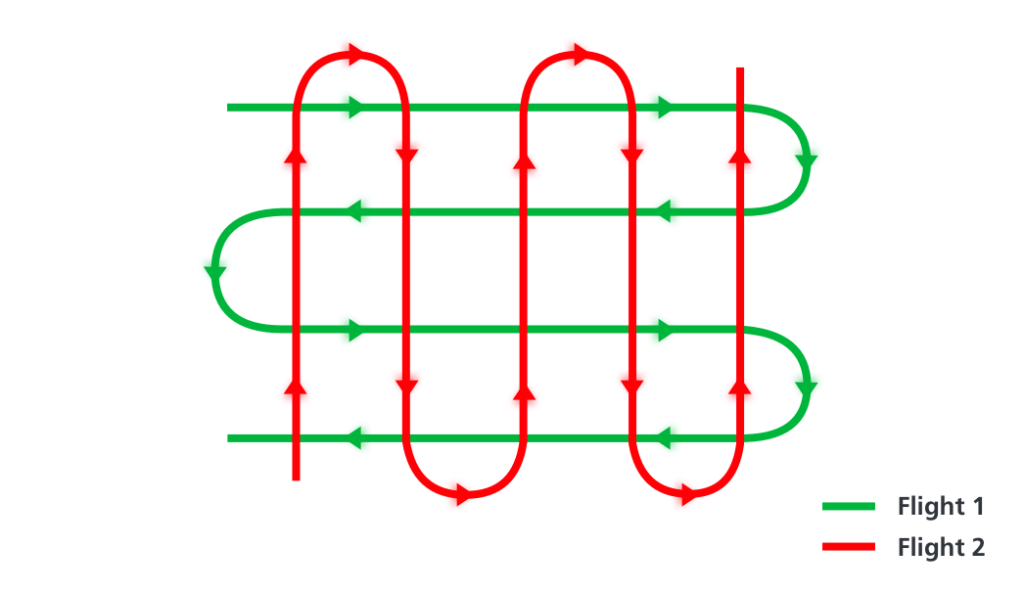
Strip adjustment can be used to adjust not only the flight lines within a flight, but also adjust multiple flights. This article shows how to use strip adjustment to more than one flight. For how to use Strip Adjustment or the method and context behind Strip Adjustment.
1. Requirements
There are two requirements needed to adjust multiple flights with Strip Adjustment.
- They must be contiguous.
- They must overlap.
Examples:
2. Recommendations on using Strip Adjustment for Multiple flights
We recommend that all the flights be performed on the same day and all the flights share the same base station. When adjusting multiple flights, there is a risk to transmit an error from one flight to the other, since the module is not able to recognize the quality of each flight. The main source of error during the trajectory processing is associated to the GNSS signals, either in the rover (sensor) or in the base station, and that is why we recommend using the same base station on the same day.
If the recommendations are not met, then a reference should be used:
- Process all the flights until LiDAR Geocoding.
- Select the flight/s that fit better with the survey conditions, trusted flight.
- Process the trusted flight on Strip Adjustment
- Perform a QC of the trusted Strip Adjusted flight.
- Process Strip Adjustment, selecting all the flights, except the trusted flight.
In the advanced settings, use the trusted flight as a reference.
3. Tips
- The flights to be adjusted can have different flight heights, speeds, sidelap or flight paths.
- If you detect that a flight has an issue, for example from the POSPac QC report, it is prudent to isolate the flight, and process this flight using another flight as reference.
- It is possible to use as reference different point cloud source. For example, mobile mapping LiDAR point cloud or a photogrammetry point cloud.
If you are looking for the step by step on how to use Strip Adjustment.
If you are looking for the method and context for Strip Adjustment, please review the article on Strip Adjustment – Method and Context