The Outliers Classifier should be used whenever the presence of gross outliers has been identified in the input point cloud during the input data verification. It can also be activated on a noisy point cloud because some outliers located close to the point cloud might not be close enough to their surrounding points to be considered as points affected only by random errors. When the Outliers Classifier detects that a point is abnormally isolated from the rest of the points.
The tool is available from LP360 v2023.3 in the Classification tab of the ribbon. It is currently licensed as an EXP feature, requiring an Experimental addon license be checked out to enable the feature.
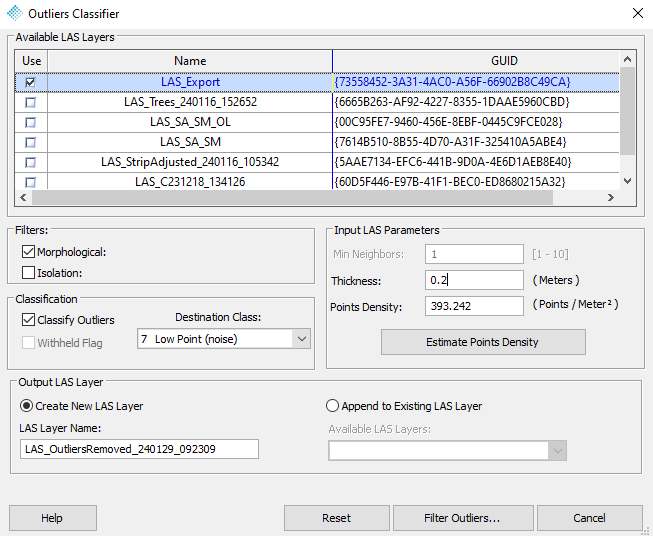
1. Outliers detection mode
Morphological rejection: This outliers rejection method is an original method, developed by Geocue. It is based on the combination of morphological and density-based indicators. The morphological indicators aim at identifying the structures inside the point cloud and score the points according to their belonging to one of the structures described by its surrounding points. The density-based ones aim at identifying isolated points, with a surrounding density abnormally low compared to one of their nearest neighbours. The combination of these indicators results in a single score, corresponding to the probability for a point to be an outlier.
Isolation based rejection: this outliers rejection method is a simple, yet efficient method of isolated points rejection. It should be used only when a dataset contains a lot of gross outliers, and not a lot of sparsely described elements in the point cloud (trees, powerlines, pole). Its functioning is very simple: every point with less than a given number of points within the “Neighbor search radius” is considered isolated. The required number of neighbors is set using the “Min. neighbor isolated points”.
The recommended method is the morphological one, because it is a complex outliers detection method, able to distinguish true outliers from locally isolated points. The results provided by this method are always superior to the ones obtained by the isolation based rejection, when the parameters are properly set (see next paragraphs). If the user does not want to perform a deep and precise outliers rejection on the point cloud, the isolation based method can be used to remove the gross outliers, located far from the rest of the point cloud.
Recommended value for TrueView 3DIS: Morphological.
2. Parameters
2.1. Min. neighbor: Minimum neighbor isolated points
This parameter appears only when the “Isolation based rejection” method is selected as outliers detection mode. It corresponds to the minimum number of points should have in its spherical neighborhood to be considered as an inlier.
Consequently, reducing the value of these parameters increases the tolerance of the filter (fewer points are removed) as the number of points to have to be considered as inlier is reduced.
In practice, the user should ensure that the points located in low density areas have a sufficient number of neighbors to be kept by this filter. Set the value according to the observed number of neighbors required to preserve inliers in low density areas. The default value is an indication but adjustments might be necessary for a majority of processing.
Recommended value for TrueView 3DIS: from 1 to 2.
2.2. Thickness: average point cloud thickness
At all times, the user must keep in mind that the “Average point cloud thickness” grossly corresponds to the resolution of the outliers classifier. Every element smaller than the selected value will be affected by the outliers classifier. If the point cloud contains very small elements that must be preserved at all costs (road cracks, low grass) the point cloud thickness should not be bigger than its size.
Effect Increasing the value of the “Average point cloud thickness” will increase the amplitude of the noise reduction. This means that the thickness of the output point cloud decreases when this parameter increases. However, the risk to create a smoothing effect also increases with the radius.
At all times, the user must keep in mind that the “Average point cloud thickness” grossly corresponds to the resolution of the outliers classifier. Every element smaller than the selected value will be affected by the outliers classifier. If the point cloud contains very small elements that must be preserved at all costs (road cracks, low grass).
Change if the noise level of the input point cloud is particularly high compared to the expected performances of the survey material used. Adjustments might also be required if the input point cloud contains a lot of irregular features and/or sharp edges. If there is an over-smoothing of essential features is seen in the output point cloud, the value reduces the value below the true point cloud thickness.
Recommended value for TrueView 3DIS: 0.2 meters or 0.7 feet, up to 0.3 meters or 1 feet
If the required precision is only a few centimetres below the original one, it is not necessary to set this value above the default value, as the noise reduction comes at the cost of a density reduction.
The value should not be lower than half the true average point cloud thickness. If the value is below this threshold, the algorithm will not be able to properly identify the geometrical features of the surface surrounding the point, and the denoised position cannot be estimated properly.
The value should not exceed 3 (three) times the true average point cloud thickness. If the value is over this threshold, the algorithm will not be able to preserve the small features of the point cloud. Then, the output point cloud will be too smoothed, and the sharp features will be affected.
How it works:outliers the measured average thickness of the point cloud is used to set the radius of the spherical neighborhood research used to compute the geometrical properties of each point.
2.3. Point density: average point cloud density
This parameter corresponds to the measured/computed average surface density of the point cloud (in pts / m²) and is used to set the number of neighbors considered during the estimation of the morphological and density-based indicators of the “Morphological rejection”.
The value must be set according to an actual evaluation of the average density of the point cloud, or according to the expected density provided by the flight planning application. It does not need to be set very precisely, as the impact of this parameter over the final result of the outliers rejection is not as important as the one the “Average point cloud thickness” on the outliers classifier result. The user should keep in mind that the required value increases with the point cloud density the value must be lowered for point clouds with a density above the expected one for a given system).
Note that these parameters also affect the tool’s capacity to identify clusters of outliers. Any cluster comprising more points than the number of required neighbors computed from the average point cloud density will not be identified as outlying, especially if it is located far from the rest of the point cloud because all the points of the cluster will be compared with other points of the cluster and not with inliers.
Recommended value for TrueView 3DIS: use the tool “Estimate Points Density” to fill automatically this value.
2.4. Classification
Classify Outliers: This option allows to put the outliers into a specific class instead of deleting them.
Recommended value for TrueView 3DIS: check the option and select as destination class “7 Low Point (noise)”.
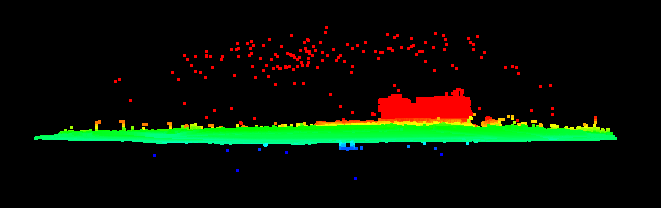
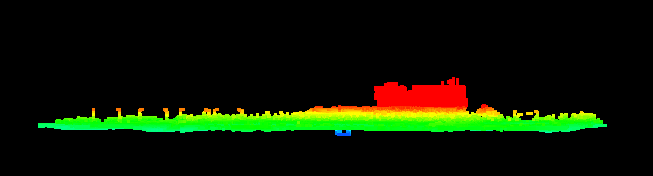
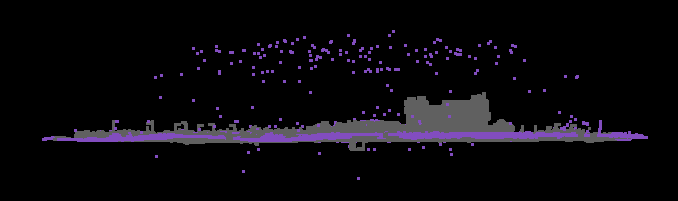
3. Output
Example of a point cloud before and after using outliers classifier
4. True View Recommendations
In the following paragraph we will provide some recommendations on how to use outliers classifier with the TrueView 3DIS workflow.
- Use this step after Strip Adjustment.
- This tool helps on the feature extraction, for example removing low points before ground classification will help to avoid “holes to hell” (round areas without ground classification).
- Default TV settings:
- Morphological
- Classify Outliers –> 7 Low Point (noise)
- Thickness: 0.2m/0.7ft
- Point Density: automatic (estimate points density)
- Large projects TV settings:
- Isolation
- Classify Outliers –> 7 Low Point (noise)
- Min. Neighbors: 1
- Thickness: 0.2m/0.7ft
- Point Density: automatic (estimate points density)
- Less time consuming than Morphological, but worse noise detection.