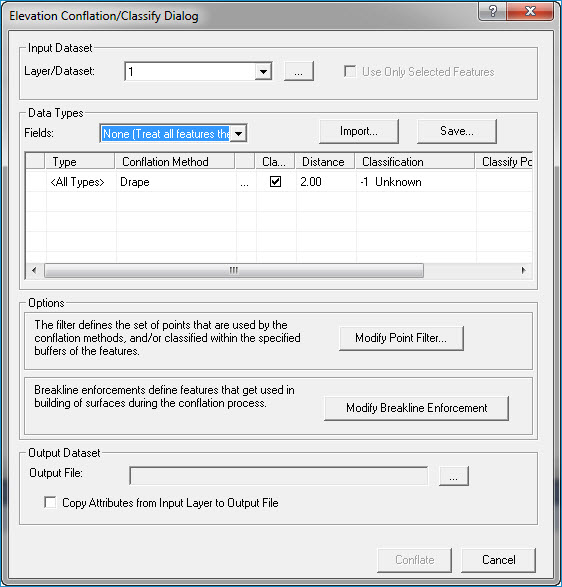

The Elevation Conflation dialog
captures the input required to conflate
elevation values (computed from LIDAR
data) to vector data such as stream centerlines, ponds, lakes, or buildings.
The exact algorithm of the conflation (i.e., conflation method) is specified
from a set of built-in methods:
Drape: drapes 2D geometry over a TIN surface created from LAS points
Downstream Constraint: drapes 2D geometry over a TIN surface created from LAS points and forces the z values in a downstream direction
Summarize Z: computes z values such as mean, minimum, maximum, or a specified constant for features or vertices
Retaining Wall: creates a bottom of wall line parallel to the input geometry and computes z values for the bottom and top of wall lines
As an optional step in the conflation process, you may classify LAS
points within a spatial relationship with
the input geometry. For example, if conflating
stream centerlines using the downstream constraint, you may also wish
to classify a buffer of points around the input stream lines for use in
breakline enforcement.
Learn
more about breakline enforcements
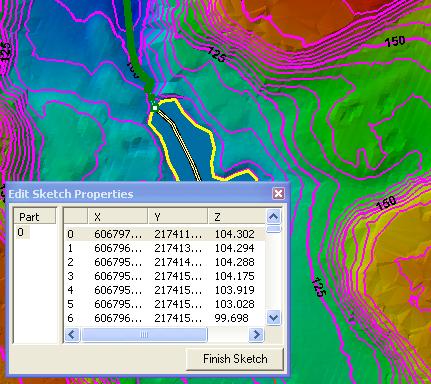
| Conflating stream centerlines using downstream constraint |
 |
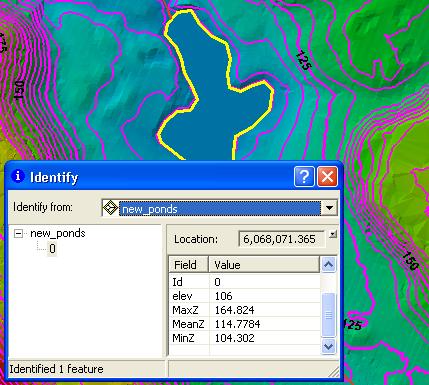
| Conflating pond and lake elevations using the Summarize Z method |
 |
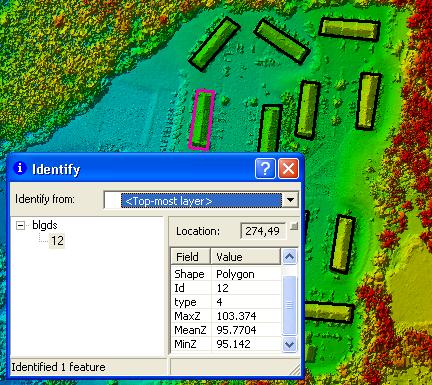
| Conflating elevations for building polygons |
 |
Learn
how to select a data set or layer
Learn
how to use selected features
Learn
how to import and save the dialog setup
Learn
how to select a type field
Learn
how to toggle the use of type values
Learn
how to select a conflation method
Learn
how to modify the properties of a conflation method
Learn
how to toggle the classification of buffers
Learn
how to modify the buffer distance
Learn
how to select a destination classification
Learn
more about classifying points within closed lines
Learn
how to modify the point filter
Learn
how to use breakline enforcements
Learn
how to select an output data set
Learn
how to copy the attributes to the output data set