A Ground Control Point (GCP) is a monumented point for which geodesic coordinates are known with a controlled accuracy and precision. It can be provided by a National Geodetic Authority or made by the user. Several topographic survey techniques can be used to determine the coordinates of a GCP (GNSS, geodetic network adjustment from distance, angle measurement, etc.). A GCP can be used for 3D accuracy assessment in surveying and mapping projects.
A LiDAR Ground Control Target (GCT) is a device that has a defined a unique center. The set of LiDAR points that impact the GCT can be used to determine this center.
We shall call the Computed GCT Center, the center of the GCT device, uniquely computed from the LiDAR points.
In comparing the Computed GCT Center and the coordinates of the GCP we can assess the deviation from the local point cloud to the GCP at the GCP location: Thus, we can compute the LiDAR point cloud accuracy. It is important to check that the estimation of the center of the GCT is conducted with sufficient accuracy. Indeed, if the center position estimation was uncertain, we could not compare with the reference GCP position. Conversely, we note that if the quality of the reference GCP position is not good enough, it cannot be used for accuracy assessment.
2D LiDAR GCTs
GCPs were first used in photogrammetry to achieve the same goal: What is the deviation between a GCP and an orthophoto produced by a photogrammetry process? The most common target used in photogrammetry for UAV collected data is the checkerboard. Another 2D Target is the concentric circle.
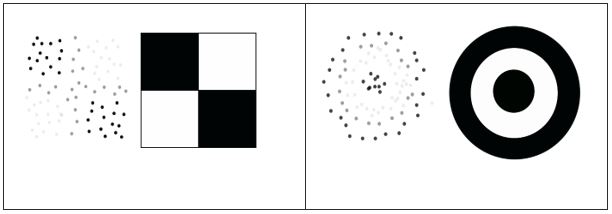
Right: Concentric Circle and typical point intensity.
When used with the 3D Accuracy add-on license in LP360, starting in v2023.2, you can achieve automated vertical and horizontal accuracy checks and improvements to your LiDAR data.
Introduction to Accuracy Star
Accuracy Star is a target specially designed for drone LiDAR projects to be installed on your tripod over your ground control points or check points. When used with the 3D Accuracy add-on license in LP360, starting in v2023.1, you can achieve automated vertical and horizontal accuracy checks and improvements to your LiDAR data.
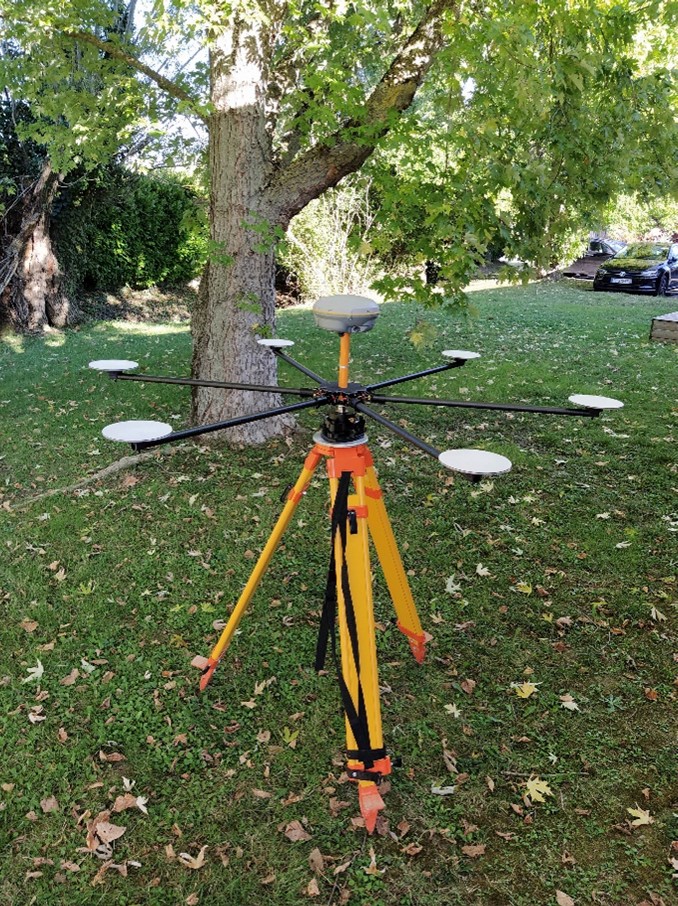

The reference position of the GCP is given by GNSS processing. The reflectors are used to compute the geometric center of the hexagon from the LiDAR point cloud.

Quality Indicators of the Accuracy Star Center Estimation
| Comments (on noise & density) | Meaning or Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reliable results | GCT is correctly estimated. |
| Noise warning | The estimated GCT center could be used for point cloud correction. Check consistency of computed offset with other GCT if possible. |
| Noise alert | Estimated GCT center location must not be used for point cloud correction. Check reference GCP position and vertical offset of GCT with respect to GCP. |
| Low density warning | Estimated GCT center should not be used for point cloud correction. Use if computed offset is consistent with other GCT/GCP offsets. Check reflector description within point cloud. |
| Low density alert | Estimated GCT center location is not reliable for point could correction. Accuracy Star description within point cloud is not good enough. |
| Not useable | GCP neighborhood does not contain any Accuracy Star. |
| Not enough points | GCP neighborhood does not contain enough points. |
| Not enough detected reflector points | GCP neighborhood does not contain enough reflector points. |
| Reflector Identification |
|---|
 |
3D Accuracy workflow using Accuracy Star, Ground Control Points and Targets in LP360
- Import Ground Control Points (GCP) from ASCII to shapefile.
- Optional: GCPs can be transformed during import so the shapefile is created in the same coordinate reference system as your project.
- Auto Find to find the Accuracy Stars in the point cloud and compare to GCPs.
- Solve translation and, if applicable, rotation correction.
- Apply Correction will apply the translation and rotation on the point cloud and create a new, debiased, LAS layer.
- Verification of the results by running Auto Find on the new LAS Layer.